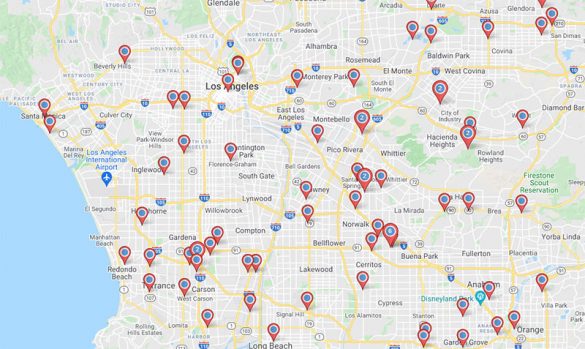
For most companies, batch geocoding is essential in establishing marketing strategies, targeting specific groups of customers, and even producing route maps to streamline operations.
If your organization is new to batch geocoding, this article will help you understand how geocoding services work, why it’s beneficial to batch geocode addresses, and how data processing through digital maps can be a game changer for your bottom line.
Table of Contents
In its most basic form, geocoding means taking your customers’ address components (like street number, street name, city, state, etc) and creating a map of their locations. To do that, your mapping software of choice will convert any address, city, state, or zip code into mappable coordinates.
“Batch Geocoding” or “Bulk Geocoding” is when you process a large number of addresses into geographical coordinates at the same time. As you can imagine, geocoding large amounts of addresses can quickly become computationally intensive, pushing most professional mapping software to charge a fee.
Two of the most common types of geocoding are Interpolation Geocoding and Parcel Geocoding–each has pros and cons, depending on your needs.
Address interpolation uses data from a geographic information system (GIS) that has mapped the street network.
Essentially, each street segment is given an address range (or block range), so interpolation geocoding can take any address you enter and match it to a street and specific segment.
This method is very successful for bigger-picture endeavors, such as establishing a sales and marketing strategy for a specific area or analyzing the competitor distribution in a given region.
On the other hand, interpolated geocoding should not be used for making decisions that require a high degree of location accuracy, such as for emergency services or rescue operations.
On the other hand, parcel geocoding requires much more granular data, which makes the service more expensive than interpolation.
Essentially, parcel geocoding considers the known boundaries of a property and then approximates the geocode in the center of that parcel.
While some may consider parcel geocoding more accurate than interpolation, the reality is that, even though it uses more granular data, parcels return data that is still very approximated since most buildings are not located in the geographic center of their property.
Reverse geocoding is exactly as it sounds, the precise opposite of geocoding. It may sound confusing, but it’s very simple.
Geocoding is the process of taking location data and transforming it into geocodes on a map, giving you an accurate visual representation of where your target audience lives.
Reverse geocoding takes the geocodes on that map (normally in the form of latitude and longitude coordinates) and transforms them into addresses.
This process is not widely used, yet, but has the potential to spawn new applications for businesses looking to extrapolate a competitive advantage from geographical data.
Maptive’s interactive mapping software includes geocoding and batch geocoding functionalities that make it easy to plot a wide range of addresses and geographical data. Thanks to the nature of Maptive’s software, you can use it with data sets of any size—whether you’re mapping 10 locations or 10,000.
Here’s how it works: after you’ve created a Maptive account (you can sign up for a free trial), upload your location dataset through an Excel spreadsheet, CSV file, or copy-paste the information directly into Maptive –then create your map to geocode your locations instantly.
Within seconds, you’ll be able to plot addresses, zip codes, cities, counties, states, landmark names, and more. Maptive allows you to automatically map thousands of locations all at once using just a list of addresses and can then bulk geocode the addresses for mapping.
Batch geocoding is integral to larger location intelligence strategies that can help regional and global companies gain a competitive edge.
From a data transformation perspective, geocoding can help improve the overall data quality of your company address fields, especially if you are uploading location data from multiple spreadsheets.
Geocoding will clean up data sets containing many addresses by removing duplicates and integrating locations with latitude and longitude coordinates for the highest accuracy during data migration.
The interactive maps that result from batch geocoding can help organizations optimize their processes, create geographic analyses and market allocations, design an effective advertising strategy, and offer the most appropriate services in specific areas.
As promised at the beginning of this article, you now have a better understanding of what geocoding is, the geocoding process, why you might want to start using geocoding services, and some practical batch geocode applications for different kinds of businesses.
Companies and organizations who integrate batch geocoding into their business practices usually leverage that information to optimize their marketing and sales efforts–and you can start doing the same for your business by selecting the right mapping software for your needs.
Maptive offers a free 10-day trial, so you can experience how using mapping for business can benefit your organization. Beyond batch geocoding, Maptive offers a full suite of mapping tools and features that can greatly benefit your marketing & sales strategy, cut out inefficiency across logistics and delivery routes, and uncover new opportunities for revenue growth.
To sign up and experience it yourself, click the link below.
Fred Metterhausen is a Chicago based computer programmer, and product owner of the current version of Maptive. He has over 15 years of experience developing mapping applications as a freelance developer, including 12 with Maptive. He has seen how thousands of companies have used mapping to optimize various aspects of their workflow.
