The dawn of geospatial technologies has dramatically altered the landscape of business operations and data-driven decision-making. By offering invaluable insights, these cutting-edge tools empower organizations to boost efficiency, slash expenses, and outpace the competition. Let’s dive into the top 10 geospatial technologies that are reshaping the business world in 2024:
Table of Contents
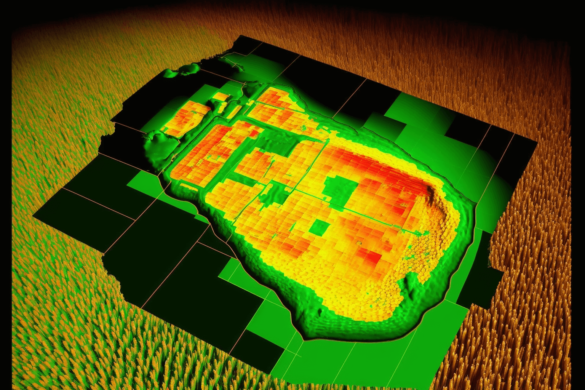
In 2024, It’s obvious more than ever before that AI has emerged as a disruptive force across many industries, revolutionizing how businesses harness and interpret data. Organizations can now mine precious insights from vast datasets, streamline decision-making, and fine-tune resource distribution through machine learning algorithms, pattern detection, and predictive analytics. For example, Descartes Labs, a geospatial analytics company, uses AI to process and analyze satellite imagery to provide insights into agricultural production, natural resources management, and urban planning. Their predictive models help industries like agriculture, energy, and finance to make data-driven decisions that improve efficiency, reduce costs, and inform long-term strategies.
Similarly, AI-powered geospatial tools such as Orbital Insight enable businesses to analyze satellite images and other geospatial data for supply chain monitoring, infrastructure development, and environmental conservation applications.
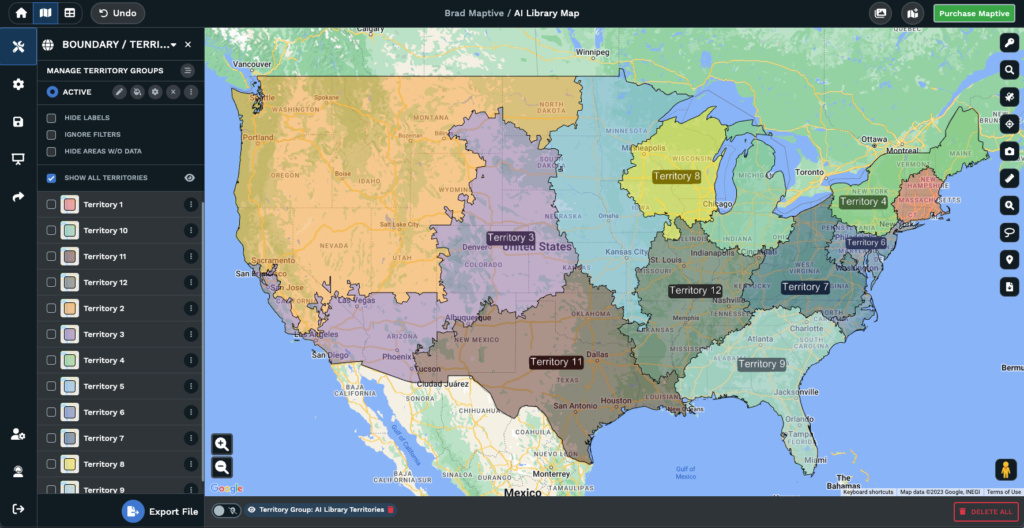
Maptive version 5 (coming mid 2024) will include an AI-based territory generation tool to simplify creating and optimizing sales territories. This innovative technology will help businesses allocate resources more efficiently, leading to improved sales and better customer relationships.
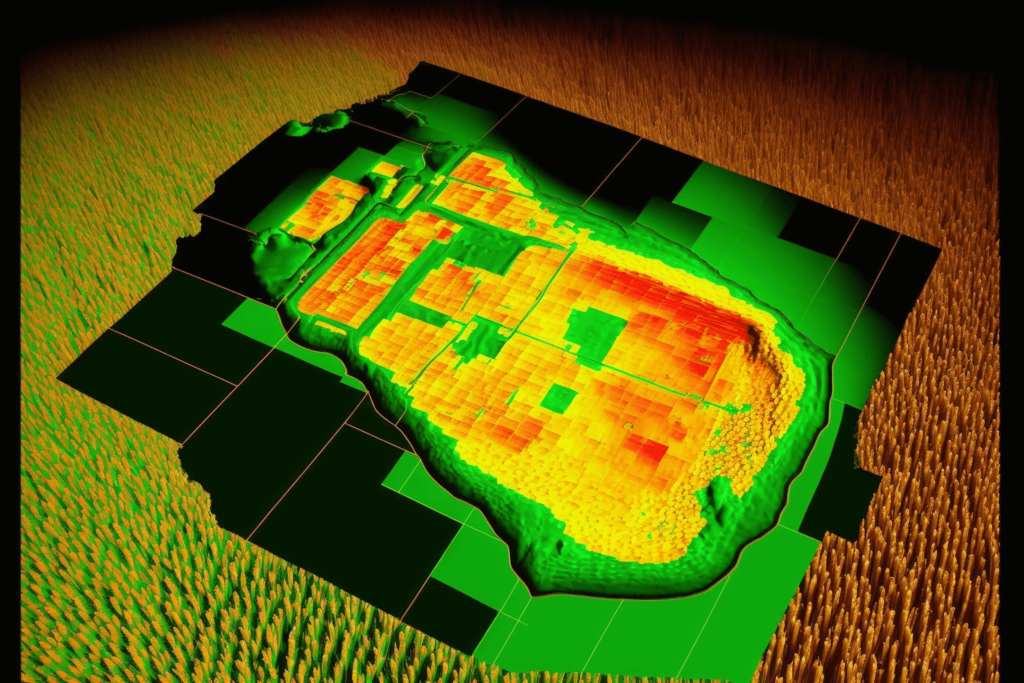
Remote sensing and satellite imagery provide up-to-date, high-resolution data for agriculture, environmental monitoring, urban planning, and infrastructure development. For instance, agriculture technology company Granular uses satellite imagery from services like Planet Labs and Maxar Technologies to monitor crop health and optimize field management.
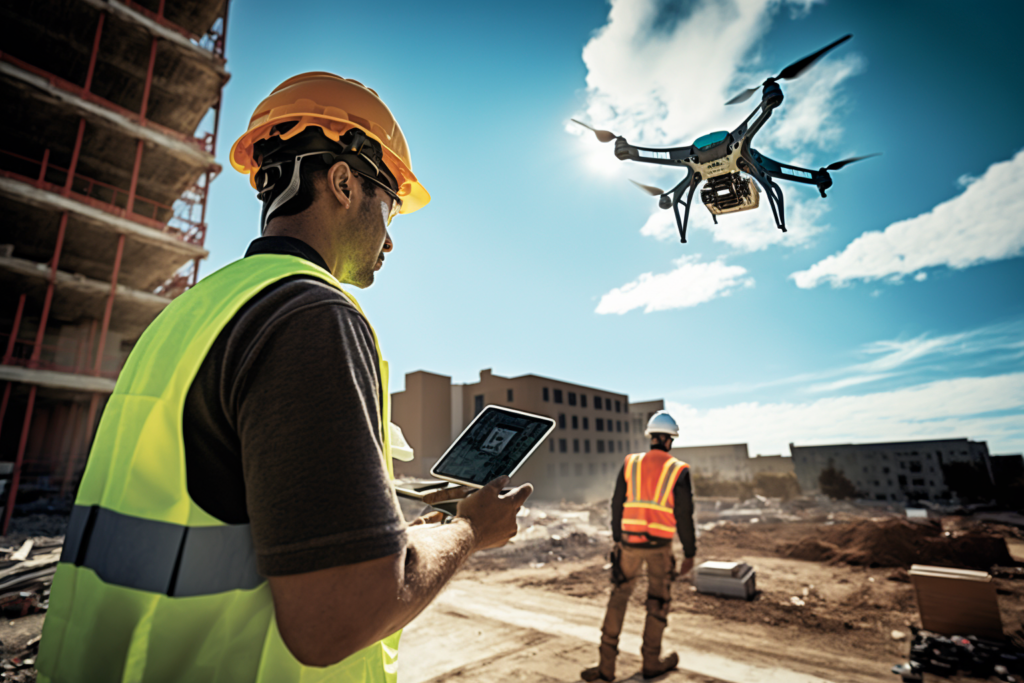
Drones have become an indispensable tool for various industries. Construction firm Skanska uses drones to capture high-resolution images and videos, monitor and inspect assets, and collect accurate geospatial data, improving safety and reducing project costs.

Location analytics is the process of deriving insights from geospatial data to make better-informed decisions. Starbucks, for example, uses location analytics to identify optimal locations for new stores by analyzing factors such as demographics, traffic patterns, and nearby businesses.
![]()
IoT devices generate vast amounts of geospatial data, enabling real-time monitoring, analysis, and decision-making. By integrating IoT data with geospatial technologies, shipping company Maersk can monitor its assets, track vessels, and optimize logistics, increasing efficiency and reducing operational costs.
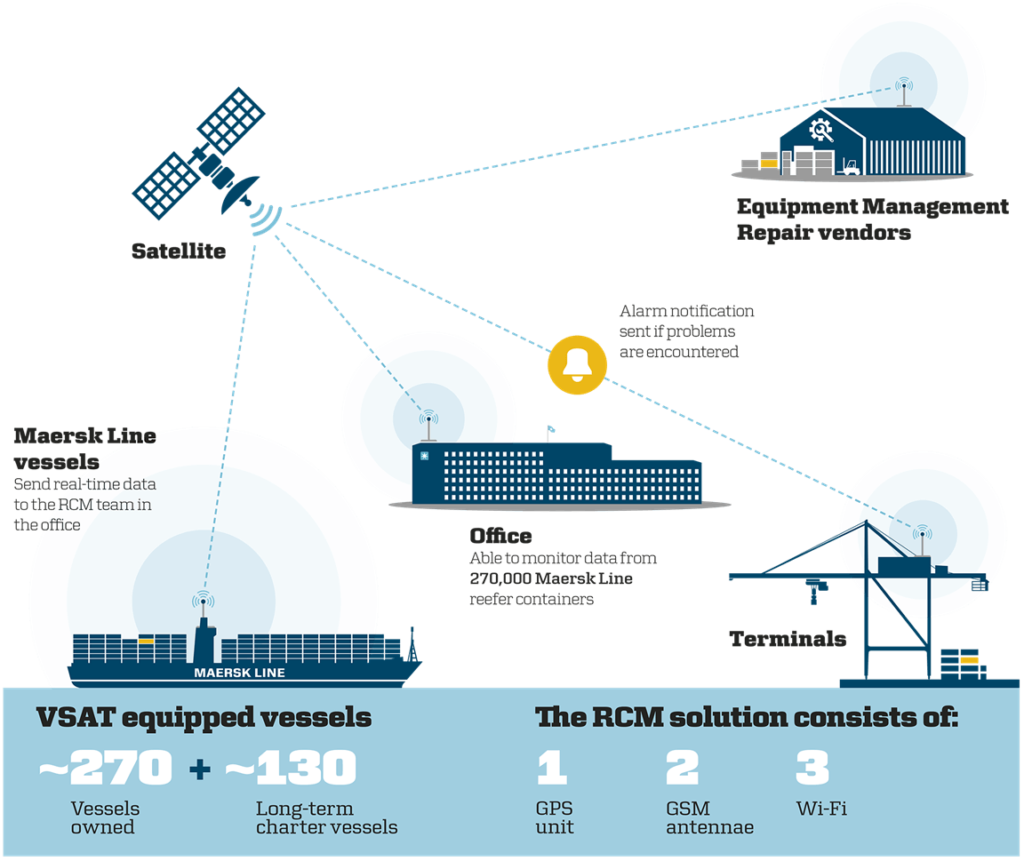
Image Source: Harvard.edu
AR and VR technologies have expanded the scope of geospatial applications, offering immersive and interactive experiences. For example, real estate company Matterport uses AR and VR technologies to create virtual tours, enabling clients to explore properties remotely and enhancing their property search experience.

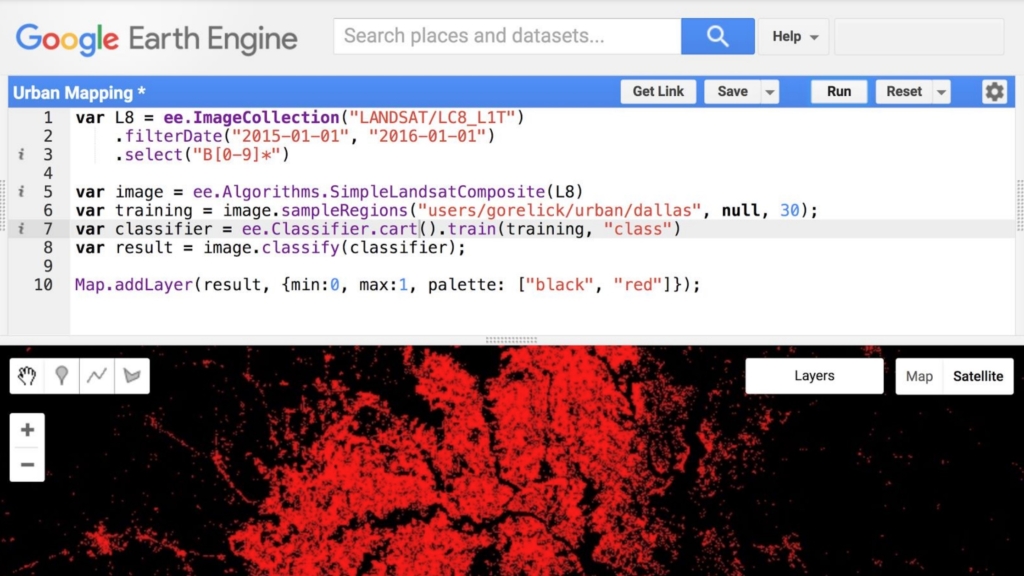
Geospatial cloud computing enables businesses to access and analyze large volumes of geospatial data without investing in costly hardware and software. For example, insurance company Swiss Re uses Google Earth Engine, a geospatial cloud platform, to assess and model natural disaster risks, informing underwriting decisions and risk management strategies.
Mobile mapping and geolocation technologies allow businesses to offer location-based services, track assets, and collect geospatial data on the go. Ride-sharing companies like Uber and Lyft use mobile mapping and geolocation to match riders with nearby drivers, optimize routes, and improve overall service efficiency. Waze, a community-driven navigation app, relies on mobile mapping and geolocation to provide users with real-time traffic information, alternative routes, and updates on road hazards, all based on input from its user community.
Open-source geospatial tools such as QGIS, PostGIS, and Leaflet offer powerful and cost-effective alternatives to proprietary software. For instance, the non-profit organization Humanitarian OpenStreetMap Team (HOT) leverages open-source tools to create up-to-date maps for disaster response and development projects in vulnerable communities.
Geospatial technologies have become essential tools for businesses to optimize operations, make informed decisions, and remain competitive in today’s data-driven world. From powerful web-based mapping platforms like Maptive to Geospatial tools like Orbital Insight, these technologies have revolutionized how companies access, analyze, and utilize geographic information. By leveraging these tools, businesses can gain valuable insights, enhance decision-making processes, and effectively address various industry challenges. As geospatial technologies evolve and become more accessible, their impact on the business world is set to increase, paving the way for a future where data-driven, geospatially informed decisions become the norm.
Fred Metterhausen is a Chicago based computer programmer, and product owner of the current version of Maptive. He has over 15 years of experience developing mapping applications as a freelance developer, including 12 with Maptive. He has seen how thousands of companies have used mapping to optimize various aspects of their workflow.
