The mapping software market ranges from free tools that plot addresses in under a minute to enterprise GIS platforms that cost tens of thousands of dollars and take months to deploy. A tool built for a developer writing navigation code into a ride-sharing app has almost nothing in common with a tool built for a regional manager balancing sales territories across six states. Ranking them on the same list, one through fifteen, is useless.
This guide organizes fifteen platforms by the problem they solve. Five categories, each with the tools that belong there and nowhere else. Pricing, limitations, and practical fit are stated plainly so you can identify your category, read that section, and ignore the rest.
Table of Contents
If you run a field sales team, a delivery fleet, or any operation where people are assigned to geographic areas, you need tools that go beyond visualization. This section covers territory creation, route optimization, CRM integration, and workload balancing.
Maptive includes over 60 tools covering heat maps, territory builders, drive-time radius calculations, demographic overlays, and multi-stop route planning. All features are available on every plan. There are no tiered restrictions where cheaper plans lose access to advanced tools. Pricing starts at $250, with team plans at $1,250. Free trials are available without a credit card.
The platform handles 200,000+ markers without performance degradation. G2 user reviews rate support quality at 9.7 out of 10. Maptive reports 99.9% uptime through 2025 with no major outages. CRM integration with Salesforce is live, and HubSpot and Zoho integrations were in testing as of late 2025.
Beta users with Salesforce report that map and data updates synchronize with a lag of under 90 seconds, providing sales teams with near-instantaneous visibility into pipeline changes. Drive-time calculations use 300% more calculation points than earlier software versions, per the company’s published data. Logistics teams in pilot programs reported routing errors down roughly 22% and fuel costs reduced by as much as 15%.
The learning curve is low for a tool with this many features. Most users report productive mapping within 30 minutes of signing up. If you manage territories and routes and do not have a GIS specialist on staff, Maptive covers the widest range of business mapping needs at a price point that does not require executive approval.
Iamge Source: Espatial.com
eSpatial has operated since 1997 and organizes its tools into three modules: eMapping for visualization, eRouting for route planning, and eTerritory for sales territory management. The modular approach means you pay for the capabilities you need rather than a bundled suite. Annual pricing starts at approximately $1,200 per user.
Territory balancing allows users to assign accounts based on workload metrics or potential sales value. The system calculates before-and-after comparisons when adjusting boundaries. Route planning includes proximity analysis and drive-time calculations. The platform integrates with Salesforce, which makes it a sensible option for organizations already running their pipeline through that CRM.
eSpatial introduced new features for 2025 for map rendering and visualization, including account-based territory optimization using the road network, specifically for field-based sales teams.
The tool is narrower than Maptive. It does not offer 60+ tools or 100,000+ data layers. What it does offer is tight, purpose-built functionality for sales operations. Teams that primarily need territory balancing and route planning alongside Salesforce data may find eSpatial more focused than a general-purpose platform.
Mapline offers a lower entry point at $330 per year for up to 20 maps. The Pro package at $660 annually unlocks custom territories and heat maps. A 7-day free trial is available.
The platform handles data import through copy-paste from Excel or spreadsheets. Once pasted, Mapline generates maps with dynamic pins where colors, sizes, and labels adjust automatically based on your spreadsheet columns. Territory creation supports auto-generated boundaries from geographic data, and the tool handles geographic complexity reasonably well for its price point.
Mapline is cheaper than Maptive and eSpatial, which makes it a reasonable entry point for smaller teams with basic territory and visualization needs. It lacks the depth of CRM integration and the processing capacity of more expensive platforms, but for organizations watching their budget, it offers real capability at a lower cost.
Map Business Online starts at $500 per year, with a $900 option that includes USA map data. Each subscription tier builds on the previous one, so upgrading adds capabilities without losing existing features. The Pro plan supports imports of up to 250,000 location records per map and creation of up to 1,500 territories per map.
The platform includes commercial-grade data: ZIP codes, street-level maps, demographic information, and business listings. Users can create maps, manage territories, run market analysis, and handle logistics within a single application. User reviews frequently mention the interface as intuitive, with people reporting productivity without prior mapping software training.
Map Business Online is designed for mid-sized operations that need territory management with baked-in US demographic and business data. If your work is US-focused and you need those datasets without paying for a separate data subscription, this is a practical choice that bundles the data you would otherwise source elsewhere.
These tools do one thing cleanly: they turn a column of addresses into pins on a map. If your primary task is making location data visible without learning new software, this is where to start.
BatchGeo has been around since 2006, and its central promise has not changed. You copy addresses from a spreadsheet, paste them into a text box on the website, and the tool plots them on a Google Maps base layer. There is no column mapping, no formatting step, and no account required for a basic map.
The free plan supports up to 250 locations with limited monthly views. BatchGeo Lite costs $15 per month for up to 15,000 locations and 3 users, while the Pro plan starts at $99 monthly with higher customization options. A prepaid annual plan at $2,499 includes 25 users and 2.5x the standard usage limits. Route optimization is available on Pro, but it caps at 25 stops per route, so organizations with longer daily routes will hit constraints quickly.
BatchGeo does not integrate with CRM systems. It does not offer territory management or demographic overlays. It was designed to be fast, and it is fast. If you need a visual of your data in under five minutes and have no interest in analysis, BatchGeo does the job. If you need anything beyond plotting and basic grouping, you will outgrow it quickly.
EasyMapMaker provides straightforward spreadsheet-to-map conversion at $29 per month. You upload a spreadsheet, and the tool generates a map with customizable pin colors, labels, and grouping options. Boundary overlays for zip codes, counties, and states are available on paid plans.
The tool is suited for small teams that need basic map outputs for internal presentations, marketing materials, or event planning. The interface is minimal, and there is not much of a learning curve. What it lacks is depth. There is no route planning, no territory balancing, no CRM connectivity, and no demographic data. If you need to produce a clean-looking map from a list of addresses and do not want to pay enterprise prices, EasyMapMaker fills that gap without complication.
Atlist is a map maker built for embedding maps on websites. You add markers manually or import addresses from a spreadsheet or CSV. Each marker can contain photos, directions, descriptions, and custom icons. The finished map is embeddable on any website and works on mobile devices.
Atlist has thousands of different map styles to choose from through an integration with Snazzy Maps, which gives users more visual control than most tools in this category. The tool targets small businesses, tourism boards, event organizers, and anyone who needs a public-facing interactive map that looks polished without involving a developer.
Atlist does not handle large datasets. It is not a GIS tool. There is no spatial analysis, territory management, or route planning. It excels at the narrow task of creating good-looking, interactive maps for the web. If you are building a store locator or a city guide, Atlist does that well and nothing more.
These platforms are not ready-to-use mapping tools. They are developer infrastructure. You need coding skills to implement them, and their value is that they give you control over every aspect of how maps function within your own product.
Mapbox holds 26.98% of the mapping and GIS software market share with over 70,000 customers, according to 6sense data. Over four million developers use the platform. Clients include Foursquare, the Financial Times, The Weather Channel, and Snapchat, per Mapbox’s own documentation.
Mapbox provides APIs and SDKs for various programming languages, including JavaScript, Python, iOS, and Android. It supports offline maps for mobile apps, turn-by-turn navigation with real-time traffic, geocoding, and address search. Mapbox Studio is the browser-based editor for designing custom base maps.
Mapbox Maps delivers 50,000 free map loads per month, with pricing at $5 per 1,000 map loads after that. Costs scale with usage. The Static Tiles API is notably more expensive than comparable endpoints from competitors, which multiple user reviews on Capterra flag as a concern.
Mapbox is the right tool when you need full control over the visual and functional behavior of maps inside your own product. A business user cannot log in and start building maps the way they would with Maptive. The platform assumes you have developers who will write code to integrate the capabilities.
Google Maps Platform provides APIs for maps, routes, and places. Pricing uses a pay-as-you-go model with a $200 monthly credit, which covers roughly 28,000 map loads or 40,000 direction calls. After the credit, costs vary by endpoint.
The Google Maps API is the most widely used mapping platform worldwide, trusted for its accuracy and integration capabilities. Its address data and satellite imagery are unmatched in global coverage. If your application requires the most recognized map interface for end users, Google Maps is the default. The tradeoff is cost at scale. Organizations with high traffic volumes report bills that climb steeply once the free credit runs out, and pricing complexity makes forecasting difficult.
Google Maps Platform is a developer tool. There is no business user interface for territory planning, route optimization, or data analysis. It powers maps inside applications. If your team is building a consumer-facing product and needs globally accurate map tiles, address search, and routing, this is the standard. If your team needs to analyze their own business data geographically, this is not the right tool.
Leaflet is a free, open-source JavaScript library for building interactive maps on the web. It weighs about 42 KB of JavaScript and works across all major browsers and mobile platforms. The library was created by Volodymyr Agafonkin and is maintained by a community of contributors.
Leaflet handles tile layers, markers, popups, and basic vector drawing. It does not include geocoding, routing, or data analysis on its own. Those capabilities are added through plugins or external APIs. The library is intentionally minimal, which makes it fast and lightweight but requires assembly to build a full-featured map application.
Organizations that want a free, highly customizable base for their own mapping applications use Leaflet. It pairs well with open tile servers like OpenStreetMap, and it integrates with Mapbox tiles or other commercial providers. If you want to avoid vendor lock-in and have developers who can build what you need from components, Leaflet gives you a clean starting point with no licensing costs.
These platforms assume a level of geospatial expertise. They handle complex spatial queries, large raster and vector datasets, coordinate systems, and workflows that go well beyond putting pins on a map. The audiences here are GIS professionals, government agencies, research institutions, and engineering firms.
Image Source: Washington University in St.Louis
ArcGIS Online is Esri’s cloud-based GIS platform, released in 2012. ArcGIS holds 26.88% of the GIS market share with over 70,000 customers. The Business Analyst Web App Standard provides tools for quick analysis, maps, reports, and infographics, and includes Esri’s global data covering 170+ countries with more than 15,000 variables. User types function as annual licenses with six different options aligned to workflows like map creation, analysis, data quality assurance, and decision support.
The platform is the industry standard for organizations that need the full weight of a GIS system. Government agencies, utility companies, urban planners, and environmental scientists use ArcGIS Online because the depth of tools and data layers matches the complexity of their work.
The tradeoffs are cost and learning curve. Enterprise pricing and the complexity of the platform create barriers for teams that need simpler solutions. User reviews consistently mention that getting productive takes meaningful time investment. If your needs are territory mapping for a sales team or quick visualization of customer data, ArcGIS is more capability than you need, and the overhead is not worth it.
QGIS is a geographic information system software that is free and open-source. It supports Windows, macOS, and Linux, and supports viewing, editing, printing, and analysis of geospatial data in a range of data formats. Development started in 2002, and the project is maintained by a global community of volunteer developers under the Open Source Geospatial Foundation. A companion mobile app, QField, has surpassed 1.4 million downloads with 500,000 active users.
QGIS supports raster, vector, mesh, and point cloud layers. It reads nearly every major geospatial file format, including Shapefiles, GeoJSON, GeoTIFF, GeoPackage, and PostGIS databases. Thousands of community-built plugins extend the base application with capabilities ranging from web map publishing to machine learning integration. In 2023, Felt became QGIS’s first flagship sustaining member, and a plugin connecting the two tools is available.
QGIS is free, which is its most obvious advantage. It provides enterprise-level spatial analysis without licensing costs. The tradeoff is technical overhead. The software requires GIS knowledge to configure and use effectively. There is no drag-and-drop simplicity, no one-click territory builder, and no customer support team. Community forums and documentation fill that gap, but organizations need staff who understand geospatial workflows.
QGIS runs on your computer’s CPU, so it is not built for analyzing millions of features or terabytes of raster data. For large-scale workloads, tools like DuckDB or Apache Sedona handle the heavy compute, and results can be visualized back in QGIS afterward. If you have GIS expertise in-house or a willingness to learn, QGIS gives you professional-grade tools at zero cost. If you need to hand a mapping tool to a sales manager on Monday and expect usable output by Friday, QGIS is not the right choice.
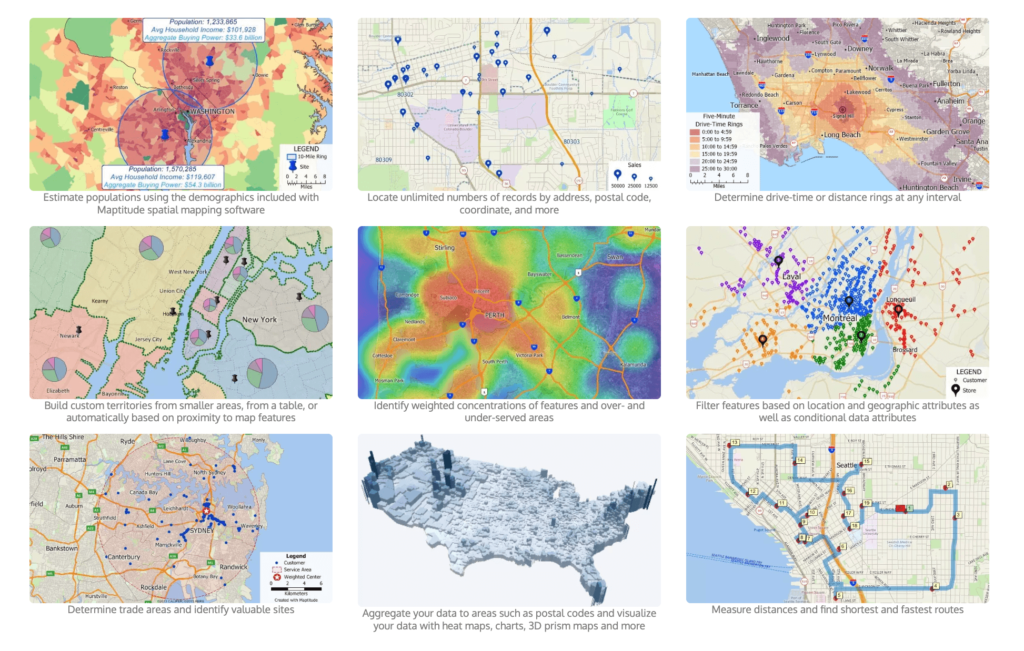
Maptitude is primarily a desktop application for map creation. While it does offer online capabilities, most customization and work occur offline on your computer. The software costs $695 per user annually for desktop access. Maptitude includes built-in demographic, economic, and geographic data for the US, and additional country data packages are available.
The platform supports territory management, drive-time analysis, route planning, and site selection. Location planning features include delivery route optimization and isochrone calculations. Map customization options cover colors, labels, legends, and premade themes.
Users report that both the cloud and desktop versions of Maptitude are difficult to master. The platform also lacks support documentation, particularly for newer updates. Maptitude occupies a middle ground between ready-to-use business tools and full GIS platforms. It offers more analytical depth than tools like Mapline or BatchGeo but less than ArcGIS. Organizations doing US-focused location analysis who want bundled demographic data without the ArcGIS price tag may find Maptitude fits their requirements, provided they can absorb the learning curve.
These platforms are built for organizations that treat geographic data as a strategic input. They connect to cloud data warehouses, support large-scale spatial queries, and serve data scientists, analysts, and business intelligence teams working with millions of records.
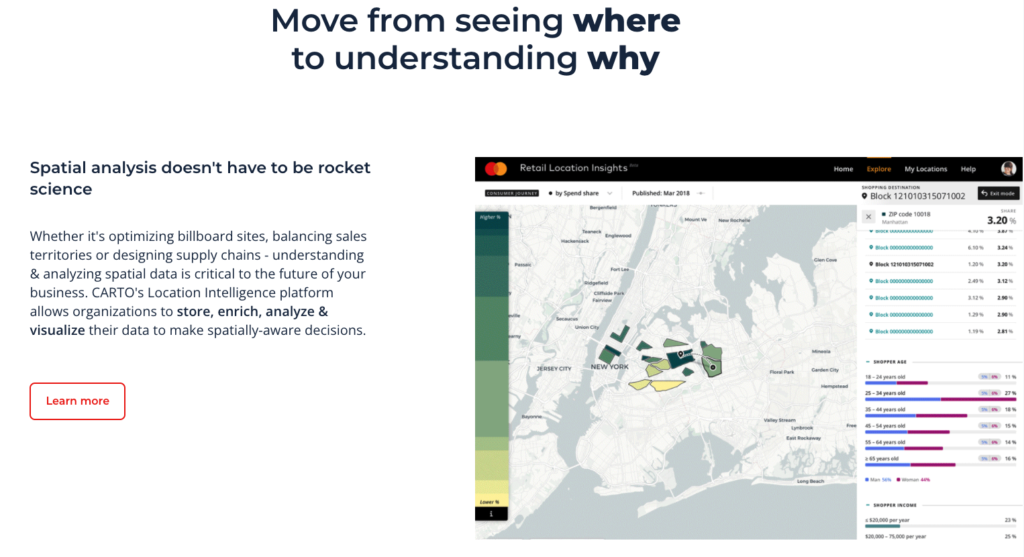
CARTO positions itself as a cloud-native location intelligence platform. Clients include Coca-Cola, Vodafone, JLL, and Deliveroo. The platform connects directly to cloud data warehouses like Google BigQuery, Snowflake, Amazon Redshift, and Databricks, which means analysis runs against data where it already lives without extraction or replication.
CARTO Workflows provides low-code, drag-and-drop tools to simplify, automate, and accelerate spatial analytics. CARTO Builder handles visualization and interactive map creation. The platform introduced AI Agents in 2025, which let non-technical users query spatial data through natural language and receive map-based answers.
The individual plan starts at $199 with 2 GB of cloud storage, 0.5 TB of daily cloud computing, and up to 100,000 map loads per month. Enterprise pricing is custom. A free 14-day trial provides access to all features.
CARTO is built for teams that already work with large spatial datasets in cloud environments. If your organization runs analytics on BigQuery or Snowflake and you need to add a geographic layer to that analysis, CARTO integrates natively. If you are a small business that wants to see customers on a map, CARTO is not designed for that task. Performance depends on how well your underlying data warehouse is structured, and advanced features like SQL-based spatial analysis take time to learn even though the interface is more accessible than traditional GIS software.
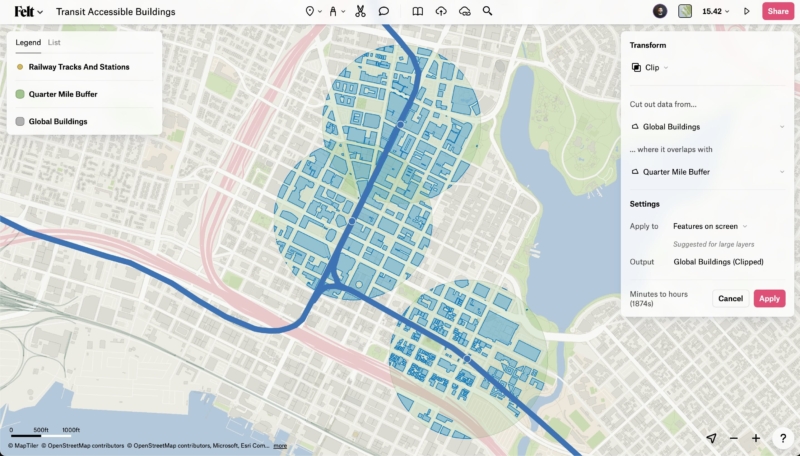
Felt launched in 2021 as a cloud-native, collaborative mapping platform. The company became the first flagship sustaining member of the open source project QGIS and introduced a plugin so QGIS users can seamlessly share work across organizations. Its customers include teams in urban planning, energy, natural resource management, disaster response, and satellite imagery analysis.
The platform processes any geospatial dataset in seconds. It accepts any file format, from Shapefile to GeoJSON. Enterprise features include database connections to Postgres, Snowflake, BigQuery, Databricks, and Amazon S3. Enterprise plans include dashboards with charts, statistics, and H3 analytics, mobile survey deployment for field teams, and custom solutions built with Felt AI.
Where typical internet maps take 30+ seconds to load after each pan and zoom, Felt loads in under 300 milliseconds. Real-time, multi-player editing is built in, which means multiple team members can work on the same map simultaneously. The platform comes with a built-in library of 50+ curated data layers and SOC 2 Type 2 compliance for organizations with security requirements.
The Team plan is ideal for teams up to 25 people, with up to 3 editors. Enterprise pricing is custom. A 7-day free trial is available.
Felt fills a space between collaborative tools like Google Docs and traditional GIS platforms. It is accessible enough for non-GIS users to contribute to and view maps, while offering spatial analysis features that GIS professionals can use in their workflows. If your organization needs to get spatial work off one person’s desktop and into a shared, live format that multiple departments can access, Felt is built for that problem.
Each section above addresses a different problem. Start by identifying which problem you actually have.
Request trials from your top two or three choices. Import your actual data, not sample datasets. Test the features you will use on a daily or weekly basis. The correct tool is the one your team will adopt and continue to use, and the only way to know that in advance is to put your real work through it before you commit.
Brad Crisp is the CEO at Maptive.com, based in Denver, CO and born in San Francisco, CA. He has extensive experience in Business Mapping, GIS, Data Visualization, Mapping Data Analytics and all forms of software development. His career includes Software Development and Venture Capital dating back to 1998 at businesses like Maptive, GlobalMojo (now Giving Assistant), KPG Ventures, Loopnet, NextCard, and Banking.
